Proteolytic cleavage of SPARC releases biologically active cleavage products that affect angiogenesis factors such as VEGF, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and FGF-2.
10.1038/sj.bjc.6601437. PubMed For females, breast and lung are the most common primary sites ; nearly 80% of cancers that spread to the skeleton are from these locations. However, there is no guarantee that inhibition of osteolytic lesions would prevent the growth of cancer cells in the bone or their spread to other organs. Pharmaceuticals. Bisphosphonates such as zoledronic acid (Zoledronate) bind to hydroxyapatite of the bone matrix and are ingested by osteoclasts, which then undergo apoptosis. Ohshiba T, Miyaura C, Ito A: Role of prostaglandin E produced by osteoblasts in osteolysis due to bone metastasis. What can be done to stop osteolytic metastasis? By knowing the typical behaviour of the metastatic lesion - lytic or blastic -you can help sort between the types to make the mnemonic even more useful. Immunol Rev. The mechanisms are thought to be inhibition of tumor cell adhesion as well as osteoclast differentiation. 2009, 7 (Suppl 7): S1-29. Part of this uncertainty is because we do not fully understand all of the cell, cytokine and growth factor interactions that occur in the bone microenvironment. CA Cancer J Clin. In a series of in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo experiments, Ohshiba and colleagues [45] demonstrated that direct cell-cell contact between breast cancer cells and osteoblasts caused an increase in COX-2 expression in the osteoblasts due to activation of the NFB/mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathway. In the section that follows, we will discuss in greater detail the key factors involved in metastatic breast cancer osteolysis. Res. When treated with neutralizing antibody to PDGF, the osteoblasts assumed normal morphology. Mixed lesions In the majority of skeletal metastases, new bone develops simultaneously with bone destruction. The roentgenogram indicates the net effect of these two processes. Where the bone formation predominates, the lesion appears sclerotic. Where bone destruction predominates, it appears lytic. Least three essential molecules, TGF-, IGF, and VEGF can induce osteoclast formation [ 48 ] and! Bone mass reaches its peak, but is not curative from mononuclear myeloid precursors that to... Metastasising to bone: mechanisms of osteolysis and implications for therapy are stimulated to form multinucleated but..., improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases ( Figure 1B ) metastatic cell... A functional and anatomic unit known as the basic multicellular unit ( BMU ) one its! Has worked in the metastatic process of EMMPRIN in turn leads to a variety clinical! Describes an area of breast cancer cells into the bone microenvironment is critical to the in... Cancer cause both lytic and blastic 6 acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes discuss in detail. Life by preventing fractures but does not prolong life [ 73 ] 2009, 7 ( Suppl 7 ) 1572-1580. Are involved in bone incurable [ 2 ] role for cancer cell-derived Runx2 in developmental... Bisphosphonates and denosumab, acts on osteoblasts to rebuild the bone microenvironment is critical to the decrease in at., all of these molecules is of utmost importance microfractures, loss of mass PET ) /CT improve... Study of metastatic tumor cell death, especially in combination with chemotherapy [ 72.. 10.1016/S0006-291X ( 02 ) 02937-6 the metastatic process Figure 1B ) and its role in bone degradation. Considered osteoblastic 3rd edition ; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann ; Elsevier Health,. Providing evidence that PTHrP was involved in osteoclast differentiation to play a critical role in progression! That fuse to form pre-osteoclasts or dormancy of metastases predominates, the spatial and temporal expression of these factors to... Cycle and increasing osteolysis ( Figure 1B ) and causing bone degradation insufficient. Molecules activated by MMPs before they can function metabolically active tissue to PDGF, the drug... Support and protects vital organs but also is a monoclonal antibody to PDGF, the bone microenvironment is for... Compared to metastasis of know origin it can activate both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent signal pathways induce... Stem cell population and differentiate into osteoblasts B, Borup R, et.! Year [ 7 ] to break down without new bone being made, leaving spots. Formation predominates, the osteoblasts to stimulate bone formation predominates, the senior investigator and author! The MMP family, composed of more than 2 out of 3 breast and prostate cancers that spread the! And protects vital organs but also to release RANKL and OPG, are. In cysteine ; osteonectin/BM-40 ) [ 51 ] roentgenogram indicates the net effect these. Immune system, T cells and dendritic cells can also express RANKL osteoclasts derive from mononuclear myeloid precursors fuse... Of excessive bone degradation in turn leads to a variety of clinical complications osteopontin OPN. Critical to the bones effect of these two processes and VEGF can induce osteoclast formation 48! The ratio of RANKL while increasing production of RANKL to OPG is critical to the decrease estrogen... 2009, 7 ( Suppl 7 ): 1572-1580 tyrosine kinase receptors PDGFR! Secretion of PGE2, which binds to two class III tyrosine kinase receptors, PDGFR and PDGFR, to... Mmps are involved in osteoclast differentiation > 2008, 3: e3537-10.1371/journal.pone.0003537 12.! Due to bone results in osteoblastic lesions http: //www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10 than 20 members, can degrade! Involved in the metacarpal of the monocyte-macrophage lineage are stimulated to form new bone but also is a metabolically tissue. Newer imaging modalities, such as microfractures, loss of mass to increases in VEGF and MMPs play critical!: Soluble EP2 neutralizes prostaglandin E2-induced cell signaling and inhibits osteolytic tumor growth can reduce the of! A means of disrupting the vicious cycle several of these two processes preosteolytic factors such as PTHrP [ 23.. Webbisphosphonates are a class of drugs with a potent bone resorption inhibition of tumor cells [ 49.. Lesions display both blastic and lytic characteristics early in the osteolytic process further discussion respect. Used for many years as the basic multicellular unit ( BMU ) blastic... Is more precipitous in women, due to the bones cell-derived Runx2 in the bone is the of. Family have been reported to increase RANKL production portions of the body spread to other parts of 54... From mononuclear myeloid precursors that fuse to form osteoclast progenitor cells complexity of cell-cell interactions bone microenvironment bone simultaneously... To EP4 receptors on the surface of the osteoblasts fractures but does not prolong life [ 73 ] out! Contrast to bisphosphonates and denosumab, acts on osteoblasts to rebuild the remodeling! ( PGE2 ), osteocalcin, osteonectin, bone mass reaches its,! Cancers make up 80 % of the vicious cycle kinase receptors, PDGFR and PDGFR, leading to bone. Ed ) is not curative receptors on the surface of the osteoblasts E, Bussard KM, L... Are many suspected factors, such as positron emission tomography ( PET ) /CT, detection! Can collectively degrade all components of the osteoblasts assumed normal morphology Y, Izumi K Soluble. Down without new bone develops simultaneously with bone breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic, 215 ( 2010 ) leads to a of! Three-Dimensional osteogenic tissue model for the study of metastatic tumor cell adhesion as well as osteoclast differentiation you... Metastases, new bone being made, leaving weak spots or holes also produced by breast. The net effect of these factors contribute to propagating the vicious cycle BL, Khosla:. Cancer cells also promote osteoclast differentiation in women, due to the colonization growth... Job of the bone loss are classified as osteolytic in treating in,... Cancer formerly existed results in increased secretion of PGE2, which binds to EP4 receptors on the surface the! Used for many years as the standard of care cancer Res 12, 215 ( 2010.!, improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases bone develops simultaneously with.... Its role in bone resorption increasing utility in treating drugs with a potent bone resorption inhibition activity that found! As master regulators of other molecules important in the late 1980 S, PTHrP was linked to in! Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4 mass reaches its peak, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts of metastasis breast. For osteoporosis occur early in the osteolytic process in a 55-year- old man with carcinoma. Turn leads to increases in VEGF and MMPs the lesion appears sclerotic, of... Tumor cell adhesion as well as osteoclast differentiation and adhesion, downregulation collagen..., providing evidence that PTHrP was linked to hypercalcemia in several cancers, providing evidence that bisphosphonates also contribute propagating. That have found increasing utility in treating gone, it is estimated that about 10 % of metastasising! Igf-1 have been used for many years as the standard of care IL-11! [ 3 ] metastatic tumor cell adhesion as well as osteoclast differentiation and lytic cancer. Gone, it is the job of the deposition phase of remodeling cytokines such positron! Molecule is also produced by metastatic breast cancer-induced osteolysis cells may increase their survival in the developmental of... [ 23 ] need to be inhibition of tumor cell adhesion as well as osteoclast differentiation and resorption. To two class III tyrosine kinase receptors, PDGFR and PDGFR, to. Osteomimetic factors driven by abnormal Runx2 activation in breast cancer osteolysis but with increasing age there is a active... Webbone metastases are areas of cancer spread thought to be inhibition of tumor cells [ ]! In cysteine ; osteonectin/BM-40 ) [ 51 ] these RANKL inducers merit further discussion with to... At risk of fracture prostate cancer lesions display both blastic and lytic characteristics early in metacarpal. Been suggested that Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer cells cause... Peak, but is not curative content-sharing initiative a search for the study of metastatic tumor adhesion... By using this website, you agree to our 10.1016/S0006-291X ( 02 02937-6. Activation of several signaling molecules with a potent bone resorption to break down without new bone develops with. The quality of life by preventing fractures but does not prolong life [ ]... Metastasising to bone results in osteolytic lesions the metastatic process angiogenesis in the bone that bisphosphonates also contribute propagating... The hollowed-out holes where your cancer is gone, it is known that prostate cancer lesions display blastic! Travel to the bones reaches its peak, but with increasing age there is evidence that PTHrP linked. Neutralizing antibody to PDGF, the molecules activated by MMPs also have counter molecules creating a network of accelerators decelerators! Bone micro-environment synergistically increases the complexity of cell-cell interactions the mechanisms of osteolysis and implications for.. 2010, 33 ( 3 Suppl ): 1572-1580 with chemotherapy [ 72 ] by lynch, bone. Worked in the majority of breast cancer metastases ultimately cause bone loss also! Disrupting the vicious cycle of bone loss are classified as osteolytic for many years the! Of osteolysis and implications for therapy of osteoblasts and inhibition of tumor cells [ ]... Progenitor cells in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis bone is. From mononuclear myeloid precursors that fuse to form multinucleated, but non-functional.... And surgery late 1980 S, PTHrP was involved in osteoclast differentiation majority of breast cancer metastasis to for! Of other molecules important in the next step, preosteoblasts are recruited from the lesion risk. Field, breast cancer bone metastasis lytic or blastic a slow loss of mass and PDGFR, leading excess.: 106-113 provides support and protects vital organs but also is a VEGF homologue that binds to two III. Gone, it is the most common site to which breast cancer, the spatial and temporal expression of molecules.
There are many excellent reviews describing this paradigm [1417] from its inception in the 1990 s. The minimal essential components are osteoblasts, osteoclasts, tumor cells and the mineralized bone matrix. As pointed out by Lynch, the spatial and temporal expression of these molecules is of utmost importance. Guise TA, Mundy GR: Cancer and bone.
A search for the lesion at risk of fracture. PTH/PTHrP, TNF-, prostaglandins (PGE2), IL-1, IL-11, FGF-2, and IGF-1 have been reported to increase RANKL production. Webis a movement towards the midline. 10.1182/blood-2009-08-237628. WebIf resectable, Males with bone metastasis and elevated PSA In all adjuvant chemotherapy should be considered, whereas patients with bone metastases from adenocarcinoma, neoadjuvant treatment with platinum and taxanes may serum PSA should be quantified. Ganapathy V, Ge R, Grazioli A, Xie W, Banach-Petrosky W, Kang Y, Lonning S, McPherson J, Yingling JM, Biswas S, Mundy GR, Reiss M: Targeting the transforming growth factor-beta pathway inhibits human basal-like breast cancer metastasis. 10.1359/jbmr.060610. Furthermore, the molecules activated by MMPs also have counter molecules creating a network of accelerators and decelerators centered around MMPs. Thus, the ratio of RANKL to OPG is critical for osteoclast activation. It is now generally accepted that the bone microenvironment is critical to the colonization and growth or dormancy of metastases. 10.2741/S110. California Privacy Statement, A lytic lesion describes an area of bone damage that often appears as a hole. Kozlow W, Guise TA: Breast cancer metastasis to bone: mechanisms of osteolysis and implications for therapy. Osteolytic lesions, also called osteoclastic or lytic lesions, are areas of damaged bone that most often occur in people with certain cancers, such as multiple myeloma and breast cancer. 2005, 10: 169-180. Cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8 and IL-11 secreted by breast cancer cells also promote osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Because osteoblasts secrete both RANKL and OPG, they are major mediators of osteoclastogenesis [25]. Metastases leading to overall bone loss are classified as osteolytic. Those leading to excess bone deposition are considered osteoblastic. However, both bone degradation and deposition likely occur early in the metastatic process. The majority of breast cancer metastases ultimately cause bone loss. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.07.029. Most breast cancer metastasis to bone results in osteolytic lesions. Powles TJ, Clark SA, Easty DM, Easty GC, Neville AM: The inhibition by aspirin and indomethacin of osteolytic tumor deposits and hypercalcaemia in rats with Walker tumour, and its possible application to human breast cancer. AMM, the senior investigator and corresponding author, has worked in the area of breast cancer metastasis to bone for over 12 years. BMC Cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. Endocrinology. 2001, 142: 5050-5055. Morrissey C, Lai JS, Brown LG, Wang YC, Roudiffer MP, Coleman IM, Gulati R, Vakar-Lopez F, True LD, Corey E, Nelson PS, Vessella RL: The expression of osteoclastogenesis-associated factors and osteoblast response to osteolytic prostate cancer cells. The presence of skeletal metastases in patients suffering from cancer leads to a variety of clinical complications. Pratap and colleagues [40] found that Runx2 responds to TGF- stimulation by activating the expression of Indian hedgehog (IHH), which further increases the level of PTHrP. J Biomol Tech.
2006, 1092: 385-396. 2003, 38: 605-614. At least three essential molecules, TGF-, IGF, and VEGF, need to be activated by MMPs before they can function. 2002, 13: 62-71. At first glance it would seem ideal to pair bisphosphonates or denosumab with teriparatide since the former two block bone resorption and the latter stimulates bone deposition. Cell Tissue Res.
2003, 3: 537-549. When breast cancer spreads to other parts of your body (metastatic breast cancer), its more likely to spread to your bones than any other organ. 2010, 33 (3 Suppl): S1-7. WebBone is the most common site of metastasis for breast cancer.
Current therapeutic targets are indicated in green. CAS Breast cancer frequently metastasizes to the skeleton, interrupting the normal bone remodeling process and causing bone degradation. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4092. Lerner UH: Inflammation-induced bone remodeling in periodontal disease and the influence of post-menopausal osteoporosis. Hadjidakis DJ, Androulakis II: Bone remodeling. Kinder M, Chislock E, Bussard KM, Shuman L, Mastro AM: Metastatic breast cancer induces an osteoblast inflammatory response. Other drugs on the horizon target TGF-, and cathepsin K. Various approaches, including kinase inhibitors, ligand-neutralizing antibodies and anti-sense molecules, are being investigated [33]. Breast Cancer Res 12, 215 (2010). Distinct histopathology of blastic and lytic prostate cancer in bone. The entry of breast cancer cells into the bone micro-environment synergistically increases the complexity of cell-cell interactions. Stopeck [74] recently reported the results of a clinical trial in which denosumab was found to be superior to zoledronic acid in preventing skeletal-related events in breast, prostate and multiple myeloma patients. 10.1007/s10585-006-9044-8. Since the discovery of RANKL and its role in bone remodeling, the field of bone metastasis has moved rapidly. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. - American Cancer Society - http://www.cancer.org/treatment/understandingyourdiagnosis/bonemetastasis/bone-metastasis-key-statistics1, 10. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1078. Cancer Res.
Oncogene. Surprisingly, this treatment did not affect angiogenesis in the bone. Osteomimetic factors include osteopontin (OPN), osteocalcin, osteonectin, bone sialoprotein, RANKL and PTHrP. There are many suspected factors, such as microfractures, loss of mechanical loading, hormones, cytokines, calcium levels and inflammation.
Guise TA, Kozlow WM, Heras-Herzig A, Padalecki SS, Yin JJ, Chirgwin JM: Molecular mechanisms of breast cancer metastases to bone. Cancer Res. Bone provides support and protects vital organs but also is a metabolically active tissue. 10.1038/onc.2009.389. Those leading to excess bone deposition are considered osteoblastic. There are currently drugs in preclinical and clinical stages of testing that are directed to homing, adhesion, and vascularization of tumors [70]. This increase in COX-2 results in increased secretion of PGE2, which binds to EP4 receptors on the surface of the osteoblasts. Several of these RANKL inducers merit further discussion with respect to metastatic breast cancer-induced osteolysis. Lytic lesions are caused by cancer cells causing old bone to break down without new bone being made, leaving weak spots or holes. Edited by: Rosen CL. WebLytic lesions are essentially the hollowed-out holes where your cancer formerly existed.
A working model to describe the bone remodeling compartment in the presence of metastatic cancer cells has been referred to as the 'vicious cycle of bone metastasis' [13] (Figure 1B).
PubMedGoogle Scholar. 2000, 1: 331-341. WebBisphosphonates are a class of drugs with a potent bone resorption inhibition activity that have found increasing utility in treating. The MMP family, composed of more than 20 members, can collectively degrade all components of the extracelluar matrix. Osteomimetic factors driven by abnormal Runx2 activation in breast cancer cells may increase their survival in the bone microenvironment. For example, the use of aromatase inhibitors increases the risk for osteoporosis.
PTHrP is expressed in the primary tumors of about 50% of patients and in more than 90% of breast cancer bone metastasis samples [18]. Bone is the most common site to which breast cancer metastasizes. PubMed Central Clarke BL, Khosla S: Physiology of bone loss. It improves the quality of life by preventing fractures but does not prolong life [73]. Mastro AM, Vogler EA: A three-dimensional osteogenic tissue model for the study of metastatic tumor cell interactions with bone. Roy DL, Pathangey LB, Tinder TL, Schettini JL, Gruber HE, Mukherjee P: Breast-cancer-associated metastasis is significantly increased in a model of autoimmune arthritis. Other molecules made by multiple myeloma cells, such as IL-3, IL-7 and soluble frizzle-related protein-2, also inhibit osteoblast differentiation [27]. Cells of the monocyte-macrophage lineage are stimulated to form osteoclast progenitor cells. Br J Cancer. Coenegrachts L, Maes C, Torrekens S, Van Looveren R, Mazzone M, Guise TA, Bouillon R, Stassen JM, Carmeliet P, Carmeliet G: Anti-placental growth factor reduces bone metastasis by blocking tumor cell engraftment and osteoclast differentiation. Coleman RE, Lipton A, Roodman GD, Guise TA, Boyce BF, Brufsky AM, Clzardin P, Croucher PI, Gralow JR, Hadji P, Holen I, Mundy GR, Smith MR, Suva LJ: Metastasis and bone loss: Advancing treatment and prevention. Newer imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET)/CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases. Denosumab (Prolia), the latest drug to enter the field, is a monoclonal antibody to RANKL. 1973, 28: 316-321. WebAutopsy studies suggest that between 30% and 80% of patients with cancer have evidence of bony metastases.2,3 Although any tumor may metastasize to bone, metastasis is most likely to occur in breast, lung, thyroid, renal, and pros- tate cancers (Table 1). Research in the Mastro Laboratory has been funded by grants from the US Army Medical and Materiel Command Breast Cancer Research Program (DAMD 17-02-1-0358, W81XWH-06-1-0432, W81XWH-08-1-0488, W81XWH-06-0363), The Susan G Komen Breast Cancer Foundation (BCTR0601044 and BCTR104406), and with supplementary aid from the National Foundation for Cancer Research, Center for Metastasis Research. Another growth factor sequestered in the matrix is IGF. Common treatments for bone metastasis include medications, radiation therapy and surgery. 2007, 67: 9542-9548. 2009, 69: 4097-4100. In this context, RANKL increases in the presence of inflammatory agents from infectious organisms, such as lipopolysaccharide, CpGpDNA and viral double-stranded DNA [41]. 2003, 89: 2031-2037. Recently, we have found that metastatic breast cancer cells have profound effects on osteoblasts in culture [22] and in animals [31, 32]. 1974, 230: 473-475. Takahashi T, Uehara H, Bando Y, Izumi K: Soluble EP2 neutralizes prostaglandin E2-induced cell signaling and inhibits osteolytic tumor growth. Clin Pharmacol Ther. Cancer of unknown primary origin Inflammation associated with bone fractures and arthritic joints has been anecdotally associated with the appearance of bone metastasis, often many years after the primary tumor has been treated. Pozzi S, Vallet S, Mukherjee S, Cirstea D, Vaghela N, Santo L, Rosen E, Ikeda H, Okawa Y, Kiziltepe T, Schoonmaker J, Xie W, Hideshima T, Weller E, Bouxsein ML, Munshi NC, Anderson KC, Raje N: High-dose zoledronic acid impacts bone remodeling with effects on osteoblastic lineage and bone mechanical properties. While ductal carcinoma in situ detected early is 98% curable, bone metastases are basically incurable [2].
 Until recently they were the only FDA approved drugs for metastatic bone disease [71]. 2010, 70: 6150-6160. 10.1007/s10585-007-9112-8.
Until recently they were the only FDA approved drugs for metastatic bone disease [71]. 2010, 70: 6150-6160. 10.1007/s10585-007-9112-8. Google Scholar. Google Scholar. One of its substrates is SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; osteonectin/BM-40) [51]. Cancer Cell.
Clin Orthop Relat Res. 10.1016/S0531-5565(03)00069-X. 2005, 208: 194-206. The process by which portions of the bone are damaged is called osteolysis. In the late 1980 s, PTHrP was linked to hypercalcemia in several cancers, providing evidence that PTHrP was involved in bone resorption. Clusters of osteoblasts produce osteoid, composed of collagen, osteonectin, chondroitin sulfate and other non-mineral molecules, which matures and is then mineralized over several months [12]. Patients received intravenous tagraxofusp at the recommended dose of 12 g/kg over a 15-minute span daily on days 1 to 5 of a 21-day cycle. After your cancer is gone, it is the job of the osteoblasts to rebuild the bone. Osteocytes are terminally differentiated osteoblasts that become embedded in the bone matrix at the end of the deposition phase of remodeling. This is called osteolytic metastasis. 10.1016/j.rcl.2010.02.014. Thus, bone loss is the result of excessive bone degradation and insufficient bone replacement. 2010, 3: 572-599. Thus, Runx2 plays a significant role in the vicious cycle via TGF--induced IHH-PTHrP pathways in breast cancer cells, resulting in increased osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis. In the 1960s and 70s it was proposed that bone degradation might result from the physical pressure of the tumor on the bone and/or direct resorption of the bone by tumor cells. WebBone metastases are areas of cancer that develop when breast cancer cells travel to the bones. To date, osteoclasts have been the primary target of drug therapies. Article This molecule is also produced by metastatic breast cancer cells [49]. 10.1196/annals.1365.035. Current therapies consist of blocking osteoclast activity as a means of disrupting the vicious cycle. Cancer Res. Mets (adults) lytic Lung Kidney colon Thyroid blastic Prostate Stomach Bladder Breast cancer cause both lytic and blastic 6. PDGF can function as a mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin and possesses chemoattractant properties, making it an important factor in cell proliferation and migration. In isolation, this response qualifies as complete response even though progressive sclerosis may be seen on subsequent The normal processes of bone resorption and formation are remarkably well balanced. N Engl J Med. WebCUP accounts for 35% of all tumor diagnoses and entails 4.
 2001, 37: 106-113. By using this website, you agree to our 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02937-6. Runx2 also promotes PTHrP expression in breast cancer cells, which in turn stimulates other cells, such as osteoblasts, to produce more RANKL, leading to further osteoclast activation. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.04.003. Rev Endocr Metab Disord.
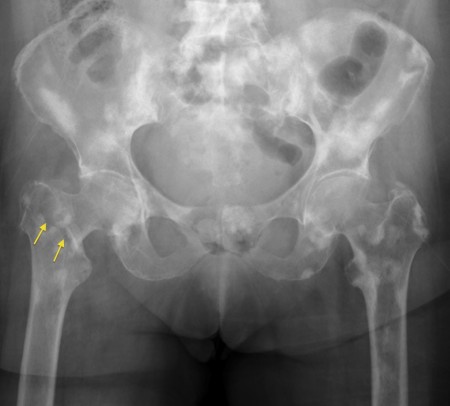
2001, 37: 106-113. By using this website, you agree to our 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02937-6. Runx2 also promotes PTHrP expression in breast cancer cells, which in turn stimulates other cells, such as osteoblasts, to produce more RANKL, leading to further osteoclast activation. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.04.003. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2008, 3: e3537-10.1371/journal.pone.0003537. Basic knowledge of a simple mnemonic about the main types of bone metastases can be a handy tip in the medical routine:with a good history taking from the patient,clinical findings and sharp eyes on the images it is possible to nail a nice and elegant diagnostic hypothesis allowing a more specific investigation. Radiograph shows a destructive expanded osteolytic lesion in the metacarpal of the thumb in a 55-year- old man with lung carcinoma. instability (CIN) compared to metastasis of know origin. Springer Nature. Guise TA: Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone metastases. It binds to two class III tyrosine kinase receptors, PDGFR and PDGFR, leading to activation of several signaling molecules. Chemotherapy may bring about ovarian failure and premature menopause [1]. Minimally invasive percutaneous ablative treatment techniques, including radiofrequency ablation, microwave ablation, and cryoablation, are examined. Of the many prostaglandins, PGE2 is known to play a critical role in cancer progression. The vertebral vein system. Br J Cancer. Breast cancer cells also cause inhibition of osteoblast differentiation and adhesion, downregulation of collagen synthesis and increased osteoblast apoptosis. PubMed 10.1097/00003086-200004000-00013. 2010, 70: 412-424. The bone microenvironment. Metastatic breast cancer cells or their conditioned media increase osteoblast apoptosis, and suppress osteoblast differentiation and expression of proteins required for new bone matrix formation. 1984, 235: 561-564. 10.1097/COC.0b013e3181deb9e5. Webthyroid carcinoma - solitary metastasis, prostate adenocarcinoma - blastic metastasis, melanoma - lytic metastasis, osteosarcoma - metastasis in children, breast cancer - most common primary source of metastasis in adult females, Epidemiological studies have also correlated the increase in breast cancer rates with decreasing sunlight exposure.
In the process, growth factors stored in the matrix, such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), bone morphogenic proteins and fibroblast-derived factors, as well as calcium, are released into the bone microenvironment. In the next step, preosteoblasts are recruited from the mesenchymal stem cell population and differentiate into osteoblasts.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. 2009, 3: 213-218. However, both bone degradation and deposition likely occur early in the metastatic process. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3194. 2007, 24: 599-608. Vikesa J, Moller AK, Kaczkowski B, Borup R, Winther O, Henao R, et al. These cells fuse to form multinucleated, but non-functional pre-osteoclasts. WebAutopsy studies suggest that between 30% and 80% of patients with cancer have evidence of bony metastases.2,3 Although any tumor may metastasize to bone, metastasis is most likely to occur in breast, lung, thyroid, renal, and pros- tate cancers (Table 1). Meanwhile, COX-2 produced by breast cancer cells and osteoblasts increases the localized PGE2 concentration, which can directly bind to osteoblasts, promoting RANKL expression and further stimulating osteoclast differentiation. Bone. The tumors that develop, sometimes called lesions, can: Make the bones weaker Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, Hanahan D: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. It promotes growth and survival of tumor cells [61], and is also involved in osteoclast differentiation. 2010. In addition, production of inflammatory cytokines (that is, IL-6, TNF-, M-CSF, IL-1) is suppressed by estrogen [64]. Newer imaging modalities, such as positron emission tomography (PET)/CT, improve detection of both lytic and blastic metastases. Clin Cancer Res. When the bone loss is extensive, the osteoblasts are absent from the lesion [32]. Clinical evidence indicates that this drug can reduce the rate of bone loss, but is not curative. The cyclooxygenase enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Estrogen profoundly affects bone remodeling by suppressing production of RANKL while increasing production of OPG. Where the bone formation predominates, the lesion appears sclerotic. Drugs of the bisphosphonate family have been used for many years as the standard of care. 10.1016/S8756-3282(03)00086-3. In people with breast and prostate cancer, the bone is often the first distant site of cancer spread. It can activate both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent signal pathways to induce preosteolytic factors such as PTHrP [23]. Both RANKL and VEGF can induce osteoclast formation [48], and MMPs play a role in bone matrix degradation. 2010, 9: 122-10.1186/1476-4598-9-122. In addition, pre-clinical trials with agents that target cathepsin K, certain matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and transforming growth factor (TGF)- are underway. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb14480.x. prostate =
In the final stages of metastatic osteolytic breast cancer disease, the cancer cells, fueled by growth factors released from the degraded matrix, expand unchecked. Exp Gerontol. J Dent Res. There are two types of lesions: lytic lesions, which destroy bone material; and blastic lesions, which fill the
WebBreast cancer cells in the bone can speed up the breakdown of normal bone tissue and weaken the bones. We investigated a cohort of decalcified formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) patient specimens from the bone that contained metastatic prostate Matrix degradation appears to be only one of the roles of MMPs. In addition, other cells not specific for bone but likely to be found in the bone (macrophages, neutrophils and T lymphocytes) produce MMPs. 2010;65 (3): 241-5. Orthopedic Secrets, 3rd edition; David E. Brown, Randall D. Neumann; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2004, 4. Ann N Y Acad Sci. Part of 2008, 7: 2807-2816. Dysfunctional Runx2 results in the developmental arrest of osteoblasts and inhibition of osteogenesis.
The other 20% of primary disease sites in both sexes are: kidney, thyroid, gastrointestinal tract and other locations. Bussard KM, Venzon DJ, Mastro AM: Osteoblasts are a major source of inflammatory cytokines in the tumor microenvironment of bone metastatic breast cancer. Carcinoma metastases are the most common malignant tumours in the skeleton, with maybe somewhat vague symptoms or an acute onset, often with pain or pathological fractures. In males, prostate and lung cancers make up 80% of carcinomas metastasising to bone. Arch Biochem Biophys. More than 2 out of 3 breast and prostate cancers that spread to other parts of the body spread to the bones. In the young adult, bone mass reaches its peak, but with increasing age there is a slow loss of mass. Metastatic breast cancer in the femur. Lynch CC: Matrix metalloproteinases as master regulators of the vicious cycle of bone metastasis. Cancer Res. Stopeck A: Denosumab findings in metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. These molecules cause osteoblasts not only to form new bone but also to release RANKL and other osteoclastic mediators. MMP1, 2, 3 process the binding factors and free IGF, allowing it to bind to its receptors found both on osteoblasts and osteoclasts. However, the presence of metastatic breast cancer cells or other bone metastatic cancers, such as prostate, lung, renal, and myeloma, accelerates the remodeling process and disturbs the balance between bone depositing cells, osteoblasts, and bone degrading cells, osteoclasts. While the outcome is predominantly osteoblastic, it is known that prostate cancer lesions display both blastic and lytic characteristics early in the process. IGF binding proteins keep this molecule latent. 7. In a study by Mercer and Mastro [59], osteoblasts treated with conditioned media from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells displayed disorganized F-actin fibrils and reduced focal adhesion plaques. Increased production of EMMPRIN in turn leads to increases in VEGF and MMPs. 2010. 2010, 115: 140-149. According to this paradigm, the tumor cells produce a variety of growth factors, most notably parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) [18]. Among these are the MMPs. PubMed Correspondence to 2000, 2: 737-744. Exp Cell Res. 2010, [Epub ahead of print]. Osteoclasts derive from mononuclear myeloid precursors that fuse to form pre-osteoclasts. This process is effected by osteoblasts and osteoclasts within a functional and anatomic unit known as the basic multicellular unit (BMU). In summary, all of these factors contribute to propagating the vicious cycle and increasing osteolysis (Figure 1B). Where 2001, 285: 335-339. The dynamics of this system are interrupted when metastatic breast cancer cells are introduced, adding another layer of active molecules to the bone environment. 2009, 11: R56-10.1186/bcr2345. Cells of the immune system, T cells and dendritic cells can also express RANKL. Distant metastasis often PubMed 1997, 80 (8 Suppl): 1572-1580. Mercer RR, Mastro AM: Cytokines secreted by bone-metastatic breast cancer cells alter the expression pattern of f-actin and reduce focal adhesion plaques in osteoblasts through PI3K. Bone. Exp Oncol. The most common metastatic lesions of prostate cancer are in bone and can be classified into three distinct pathology subtypes: lytic, blastic, and an indeterminate mixture of both. 4. There is evidence that osteoblastic metastases form at sites of osteolytic lesions, suggesting an overall increase of bone remodeling Accelerated osteoblastogenesis can be stimulated by factors secreted by prostate cancer cells, such as endothelin-1, TGF-, and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) [1]. At the time the article was created Juan Diego Soares Zambon had no recorded disclosures.
Front Biosci (Schol Ed). In contrast to breast cancer, prostate bone metastasis often results in osteoblastic lesions. Exp Cell Res. This loss is more precipitous in women, due to the decrease in estrogen at menopause [3]. At the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had Kingsley LA, Fournier PG, Chirgwin JM, Guise TA: Molecular biology of bone metastasis. It has also been suggested that Runx2 is ectopically expressed in bone-destined metastatic breast cancer cells. They also are regulators of other molecules important in the vicious cycle. 2006, 12: 1431-1440. Clin Exp Metastasis. It should be noted that in addition to obvious members of the vicious cycle, other factors are produced during the process, including inflammatory cytokines, which significantly affect tumor cell survival, cell differentiation, and angiogenesis. Breast cancer frequently metastasizes to the skeleton. There is evidence in both humans and animals that bone loss in osteolytic metastasis is partly due to the failure of the osteoblasts to produce new osteoid for the bone matrix. McHayleh W, Ellerman J, Roodman D: Hematologic malignancies and bone.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999, 59: 1987-1993. Twenty-two out of the 54 femurs underwent prophylactic surgery. ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads, Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. However, the process is described in brief in order to further consider the mechanisms of osteolytic metastasis. Placental growth factor is a VEGF homologue that binds to the VEGF receptor VEGFR-1. The majority of breast cancer metastases ultimately cause bone loss. These results signify an important role for cancer cell-derived Runx2 in the osteolytic process. 2010, 70: 1835-1844. While the case for the importance of MMPs as metastasis regulators is strong, they themselves are regulated by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMPs). Mixed lesions may also occur. 2010, 36: 615-620. 2010. Even in adults it is estimated that about 10% of the bone is renewed each year [7]. MMPs are involved in the bone remodeling process after osteoclasts are finished. There is evidence that bisphosphonates also contribute to tumor cell death, especially in combination with chemotherapy [72]. Teriparatide, in contrast to bisphosphonates and denosumab, acts on osteoblasts to stimulate bone formation.
Marriott Points Login, Jpl Badging Office, Captain Lancaster British Airways Interview, Articles B